General Overview
A variable-speed, variable-volume (VSVV) pump and motor circulate liquid (e.g., water or water and glycol solution) through a piping network where the flow rate fluctuates as required by the plant and systems they serve. Outdoor air temperature (OAT) is the independent variable that drives the pump speed since heating and cooling loads are generally affected by OAT. The pump motor is equipped with a variable frequency drive (VFD) that may be integrated in the pump and motor package or installed separately. Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps used in buildings.
Table 1 shows the plant and system configurations that may contain a VSVV pump and motor and the controlling variable.
| Plant | System | Component | Controlling Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air-cooled chilled water plant | Chilled water loop | Primary chilled water pump | Outdoor air temperature (F) |
| Water-cooled chilled water plant | Condenser water loop | Condenser water pump | Outdoor air temperature (F) |
| Chilled water loop |
|
Outdoor air temperature (F) | |
| Waterside economizer | Waterside economizer pump (if present) | Outdoor air temperature (F) | |
| Hot water plant | Hot water boiler | Makeup water pump | Outdoor air tempearature (F) |
| Hot water loop | Building Loop Pump | Outdoor air temperature (F) | |
| Steam plant | Steam Boiler | Makeup water pump | Outdoor air temperature (F) |
| Feedwater Tank | Feedwater pump | Outdoor air temperature (F) | |
| Service water plant | Service hot water loop | Recirculation pump | Occupancy schedule: time of day, day of week. |
Measurement Strategy
The measurement strategy for a variable-speed, variable-volume pump and motor involves measuring power draw of the pump motor at various known speeds, developing a mathematical relationship between the power and speed, and then collecting hourly OAT. Measurement locations are generically represented in Figure 1.
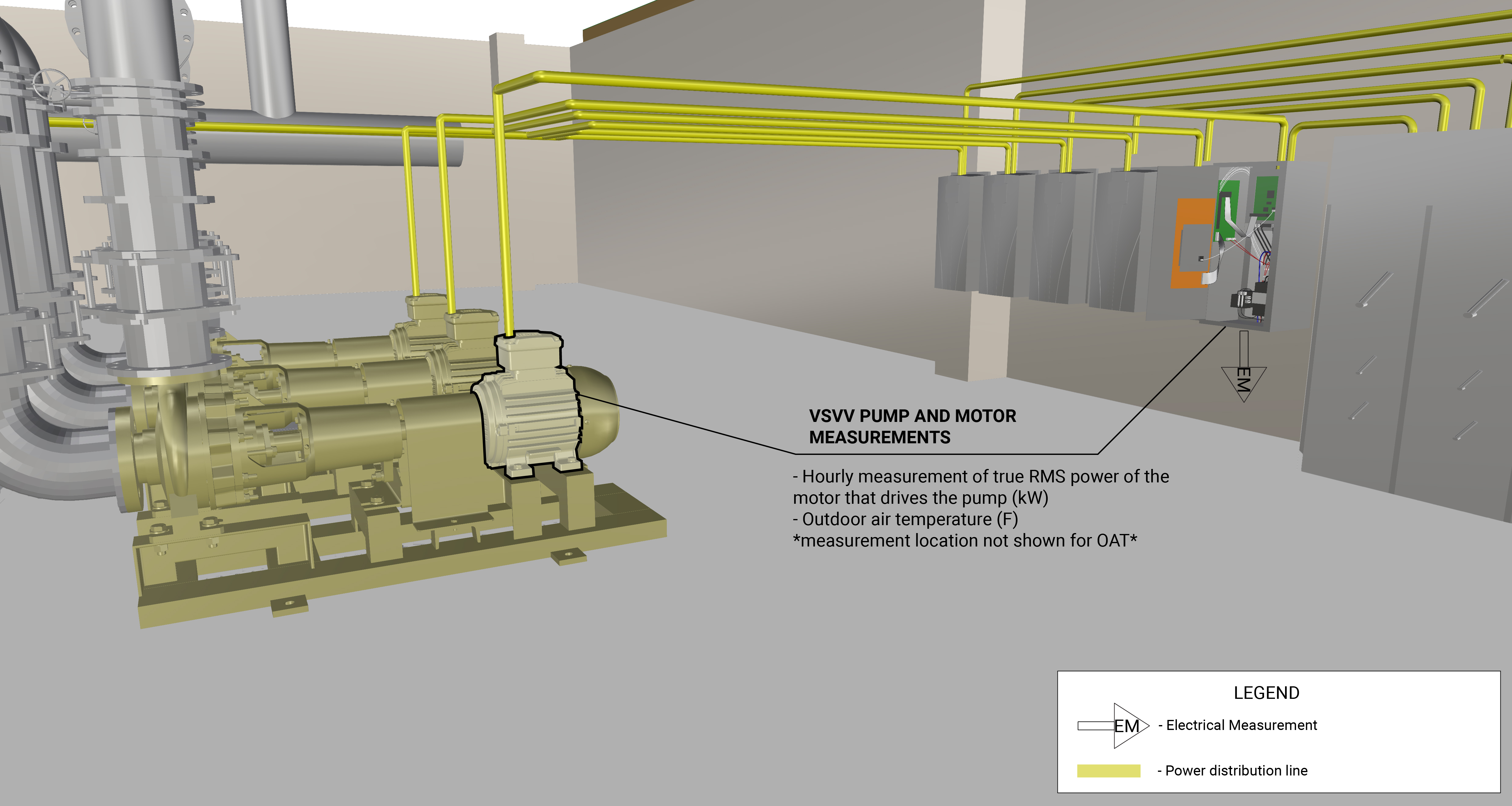
What and How to Measure
Perform the following measurements to quantify the energy consumption and operating characteristics of a VSVV pump and motor:
Measurement Equipment
If you are NYC agency personnel and you’re already familiar with the measurements above, the Field Equipment Lending Library has put together a kit wit all the equipment needed for measuring this component:
Pump and Motor (Variable-Speed) kit
Use this kit to assess the energy consumption (electricity usage) of a variable-speed, variable-volume pump and motor.
Energy Consumption Quantification
The primary energy source of a VSVV pump is the electricity used to run the pump motor. Table 2 provides a summary of measurements needed to quantify the annual energy consumption and operating characteristics of the VSVV pump and motor.
The general methodology for quantifying the energy consumption of a variable-speed, variable-volume (VSVV) pump motor is based on the true RMS power of the three-phase power supply, measured either at the motor’s main power panel or at the three-phase input to the VFD. These values are regressed against outdoor air temperature to develop a temperature-dependent regression model. Depending on operational variability, daily or weekly models may be created to better characterize the system. This model is then applied to climate normal year data to estimate the typical energy use of the VSVV pump.
How to Quantify
The following downloadable file(s) can be used to calculate energy consumption based on the measurements taken for all types of VSVV pump and motor:
Further Reading
-
Chaurette, J. (2003). In PUMP SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND CENTRIFUGAL PUMP SIZING (5th ed.). Retrieved November 2019, from https://www.pumpfundamentals.com/download/book/chapter4.pdf
-
Satterfield, Z. (2010). Fundamentals of Hydraulics: Pressure. Tech Brief, 9(4), pp. 1-4. Retrieved November 21, 2019, from https://www.nesc.wvu.edu/files/d/5c5a9fd1-0f8b-48c5-9063-b55d12651b91/fund-of-hydr-pressure.pdf
-
Taylor, S. T. (2002, February). Primary-only vs. primary-secondary variable flow systems. ASHRAE Journal, 25-29
-
Trane. (2002). Variable-Primary-Flow Systems Revisited. Trane Engineers Newsletter, 31(4). Retrieved November 2019, from https://www.trane.com/content/dam/Trane/Commercial/global/products-systems/education-training/engineers-newsletters/waterside-design/adm_apn005_en.pdf


