General Overview
A compressor is one of the main components of a chiller. A constant-speed compressor operates at a constant speed to raise the vapor pressure of the refrigerant and power the refrigeration cycle of the chiller.
| Plant | System | Component |
|---|---|---|
| Air-cooled Chilled Water Plant | Air-cooled Chiller | Chiller Compressor |
| Water-cooled Chilled Water Plant | Water-cooled Chiller | Chilled Compressor |
Evaluation of Energy Transfer
The primary energy source for a constant-speed compressor is the electricity used to run the compressor motor. Table 2 provides a summary of measurements needed to quantify the annual power consumption and operating characteristics of the constant-speed compressor and motor.
| Component Quantification | Values to be Quantified | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity usage of a constant-speed compressor motor |
|
|
Measurement Strategy
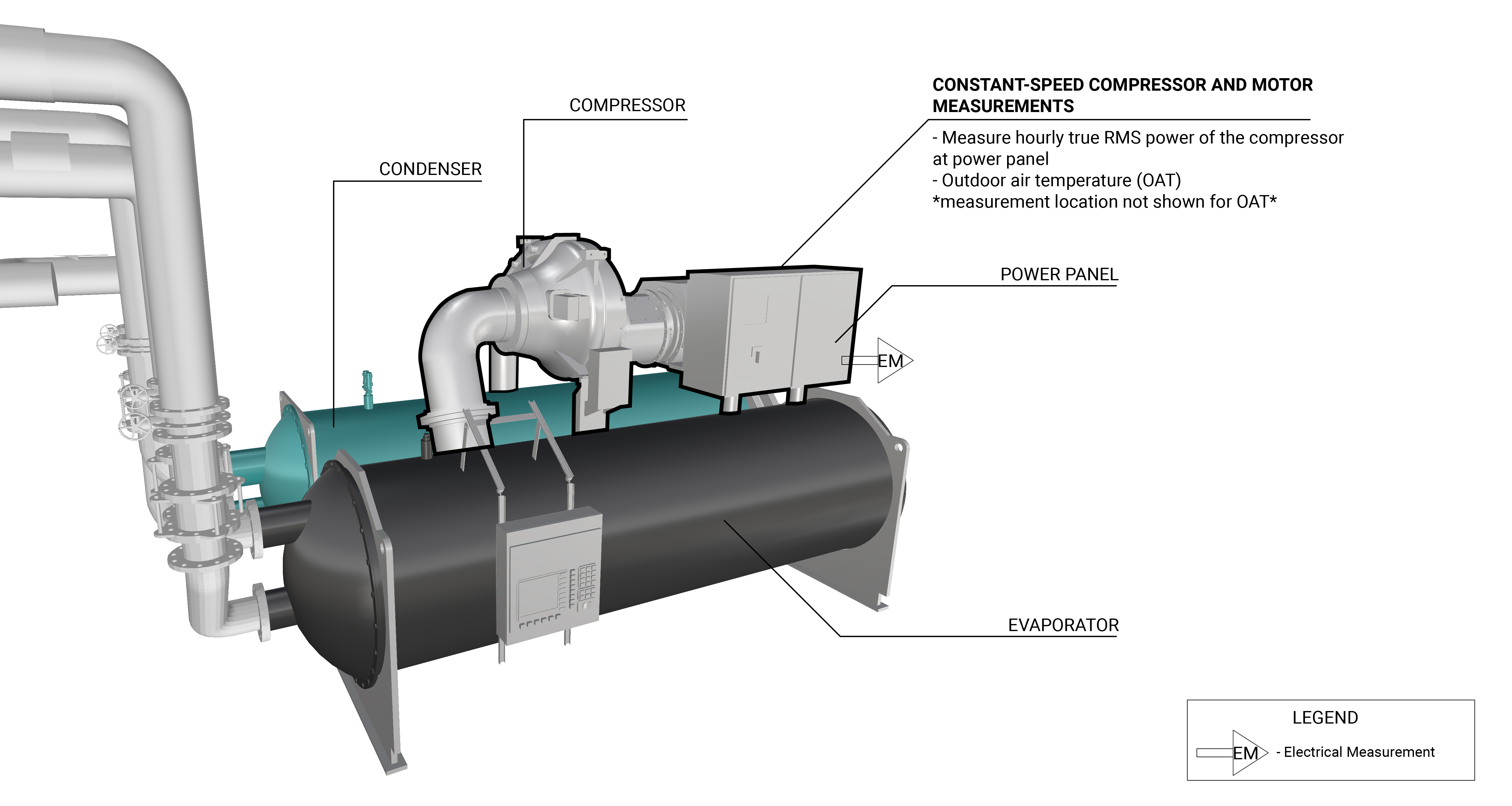
The measurement strategy for a constant-speed compressor and motor is to do a one-time Measurement Strategy. The measurement strategy for a constant-speed compressor and motor is to do a one-time measurement of the power draw and long-term measurements of the operational schedule of the motor. The approach assumes that the power draw stays constant throughout the measurement period. Because the motor runs at constant speed and is under a constant load, it is either operating at full power (when on) or it is drawing no power (when off).
A motor on/off data logger is used to record the operating schedule. The true RMS power is measured at main feed to the constant-speed motor. Measurement locations are generically represented in Figure 1.
Measurement Equipment
| Equipment | Description | Measurement (Units) |
|---|---|---|

DENT 16” RoCoil Flexible Rope Current Transformers (CT-R16-A4-U) |
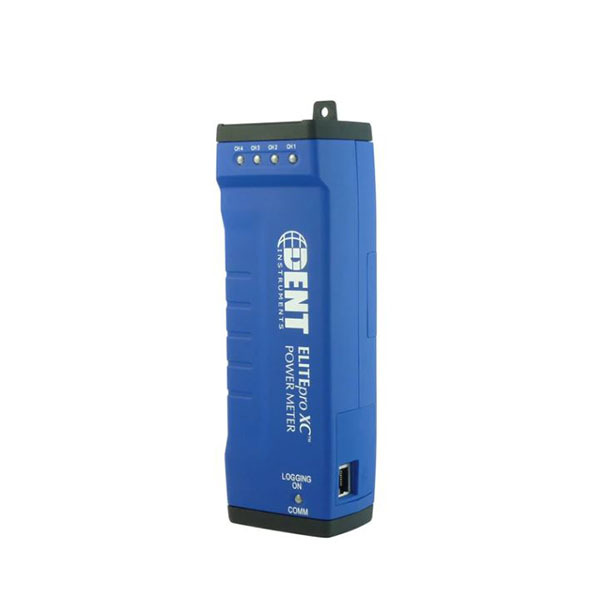
Provides a measurement of true RMS power from voltage and current inputs and records long-term power (kW) and energy (kWh) measurements. Requires ELOG19 software and a USB connection cable for programming and downloading data files. | True RMS Power (kW) |

|
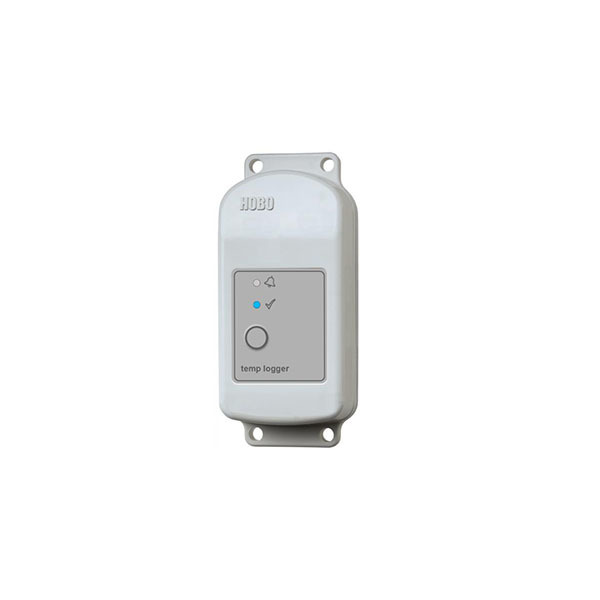
Records outdoor air temperature and relative humidity using internal sensors. Requires HOBOware software and a USB connection cable for programming and downloading data files. |
Further Reading
- ASHRAE. (2020). HVAC Systems and Equipment. Atlanta, GA: ASHRAE.


