General Overview
Air-to-air heat exchangers transfer energy between two airstreams that must be at different temperatures for sensible heat transfer and different moisture contents for latent heat transfer.
In a building, an air-to-air heat exchanger can be used to recover latent or sensible heat during the cooling or heating season. Recovering energy from the exhaust stream lessens the energy load on the air handling plant. Typical air-to-air heat exchangers include fixed plate heat exchangers and rotary wheel heat exchangers, with the former typically only recovering sensible heat. Table 1 shows the plant and system configurations that may contain an air-to-air heat exchanger.
| Plant | System | Component | Controlling Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Handling Plant | AHU with Heat Recovery Unit | Fixed plate or rotary wheel heat exchanger | Outdoor air temperature (F) |
| A dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) | Fixed plate or rotary wheel heat exchanger | Outdoor air temperature (F) |
Measurement Strategy
The measurement strategy for an air-to-air heat exchanger is to measure the heat transfer (Btu/h) from airstream to airstream within the heat exchanger, as well as any energy consuming components associated with the heat exchanger, such as the energy wheel motor.
Figure 1 shows the measurement locations in a fixed plate heat exchanger.
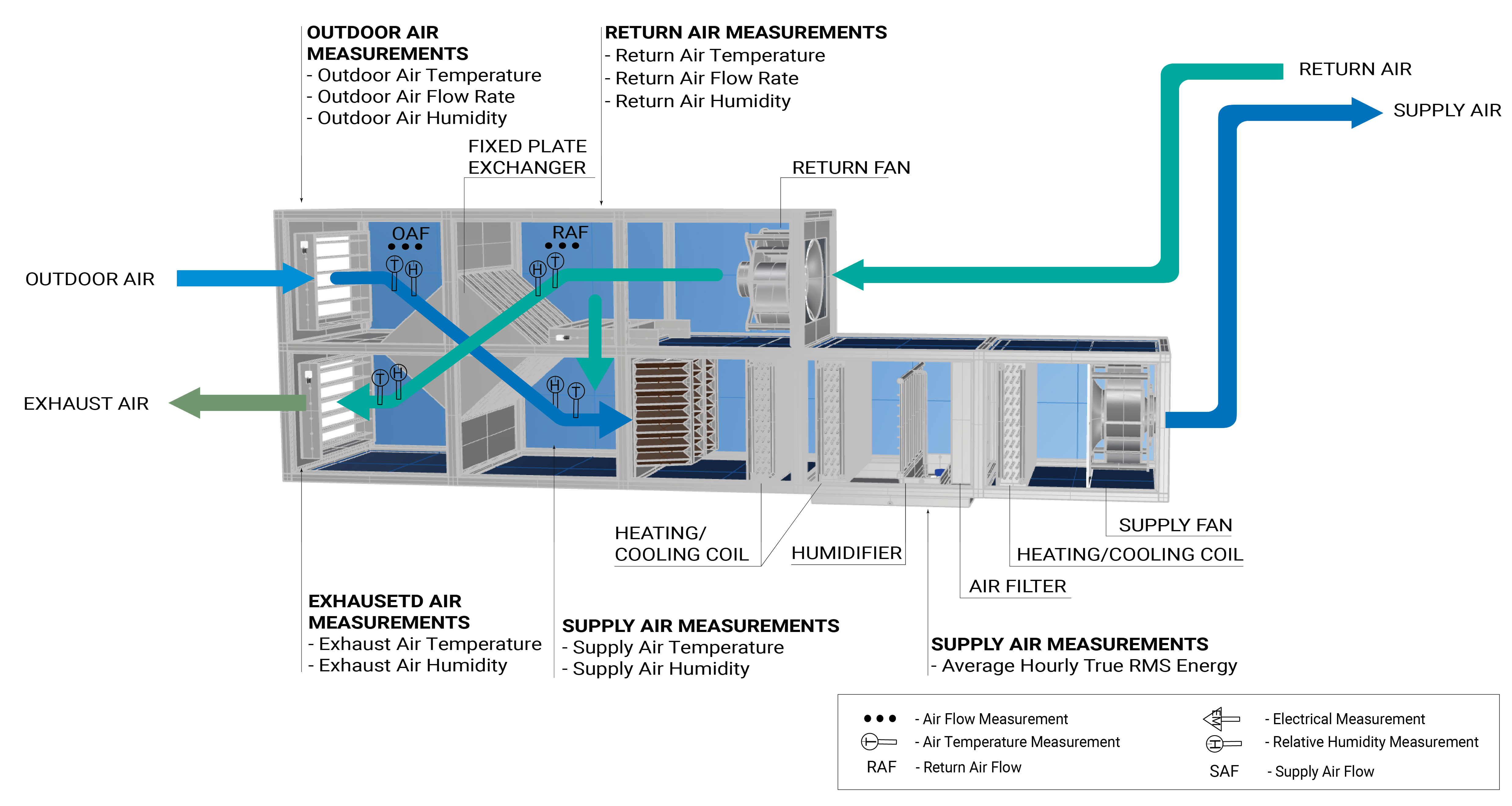
Figure 2 shows the measurement locations in a rotary wheel heat exchanger.
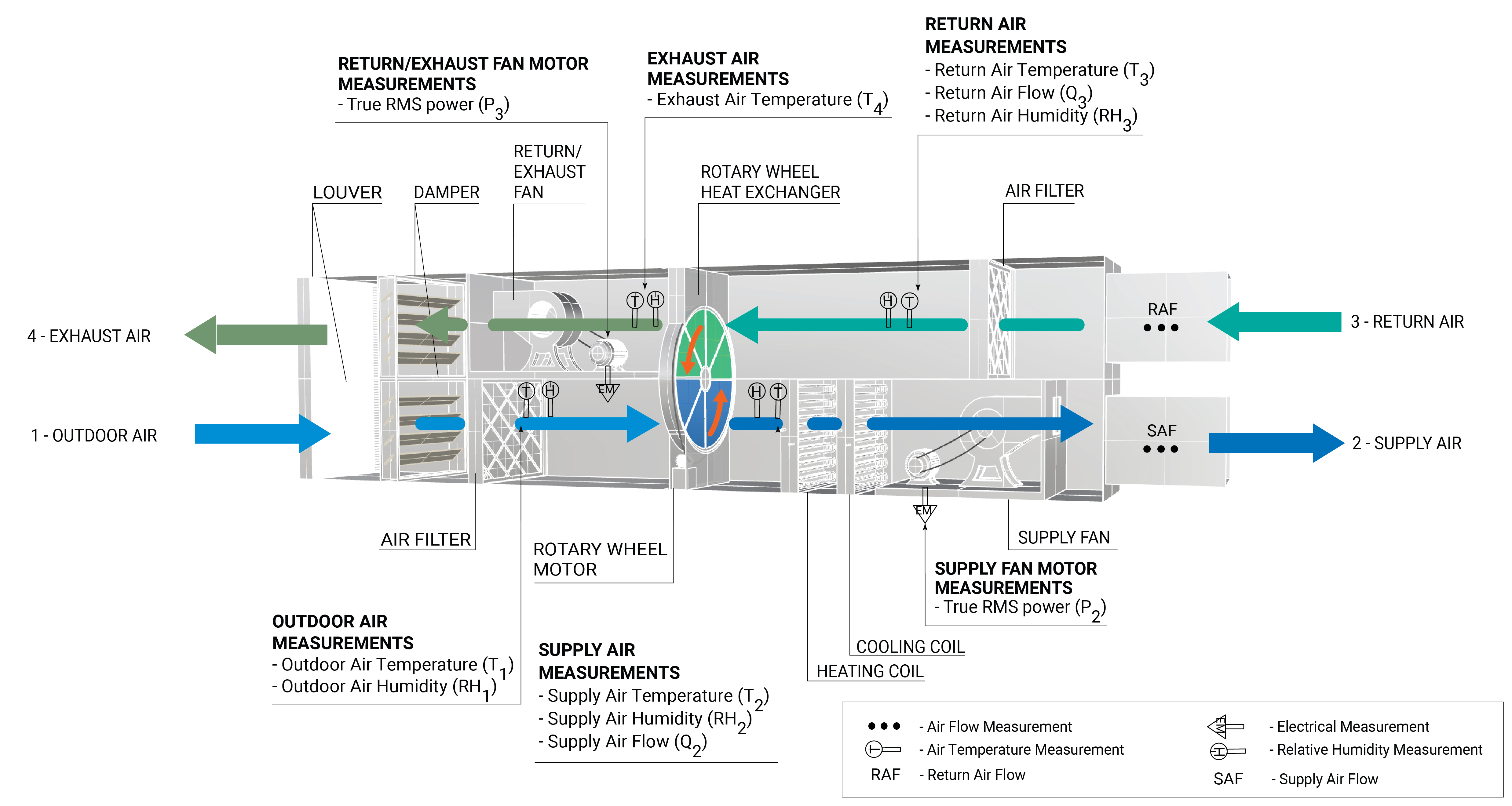
What and How to Measure
Perform the following measurements to quantify the annual energy consumption and operating characteristics of an air-to-air heat exchanger:
Measurement Equipment
If you are NYC agency personnel and you’re already familiar with the measurements above, the Field Equipment Lending Library has put together a kit wit all the equipment needed for measuring this component:
Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger kit
Use this kit to assess the heat transfer of a rotary wheel air-to-air heat exchanger.
Energy Consumption Quantification
The general methodology for quantifying the energy impact of an air-to-air heat exchanger is to determine the temperature differential on the supply side of the heat exchanger and the supply airflow. If latent energy is also transferred, this is determined by the humidity differential across the heat exchanger. The supply flow rate can be measured or assumed, depending on available resources. These energy transfer values can be regressed against a controlling variable (such as outdoor air temperature) to develop a regression model. Depending on the variability of operations, daily or weekly models may be developed to better characterize the component.
How to Quantify
The following downloadable file(s) can be used to calculate energy consumption based on the measurements taken for this component:
Further Reading
-
ASHRAE (2020). “ASHRAE Handbook: HVAC Systems and Equipment,” Chapter 1. HVAC SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND SELECTION. I-P Edition.
-
ASHRAE (2020). “ASHRAE Handbook: HVAC Systems and Equipment,” Chapter 26. AIR-TO-AIR ENERGY RECOVERY EQUIPMENT. I-P Edition.
-
CenterPoint Energy (2022). “Runaround Loops.” Energy Recovery Systems. https://www.centerpointenergy.com/en-us/Services/Pages/Runaround-loops-MN.aspx?sa=MN&au=bus
-
Heatex (2022). “Heat Exchanger Basics.” https://www.heatex.com/knowledge/heat-exchanger-basics.


