General Overview
A compressor is one of the main components of a chiller. A compressor can operate at a constant or variable speed to raise the vapor pressure of the refrigerant and power the refrigeration cycle of the chiller.
| Plant | System | Component |
|---|---|---|
| Air-cooled Chilled Water Plant | Air-cooled Chiller | Chiller Compressor |
| Water-cooled Chilled Water Plant | Water-cooled Chiller | Chiller Compressor |
Measurement Strategy
The measurement strategy for a compressor and motor involves taking hourly measurements of the power draw of the motor with an energy logger. The logger will continuously monitor the hours of operation and amount of electricity used by the compressor. If the compressor is part of a chilled water system the outdoor air temperature should be measured in hourly intervals. Measurement locations are generically represented in Figure 1.
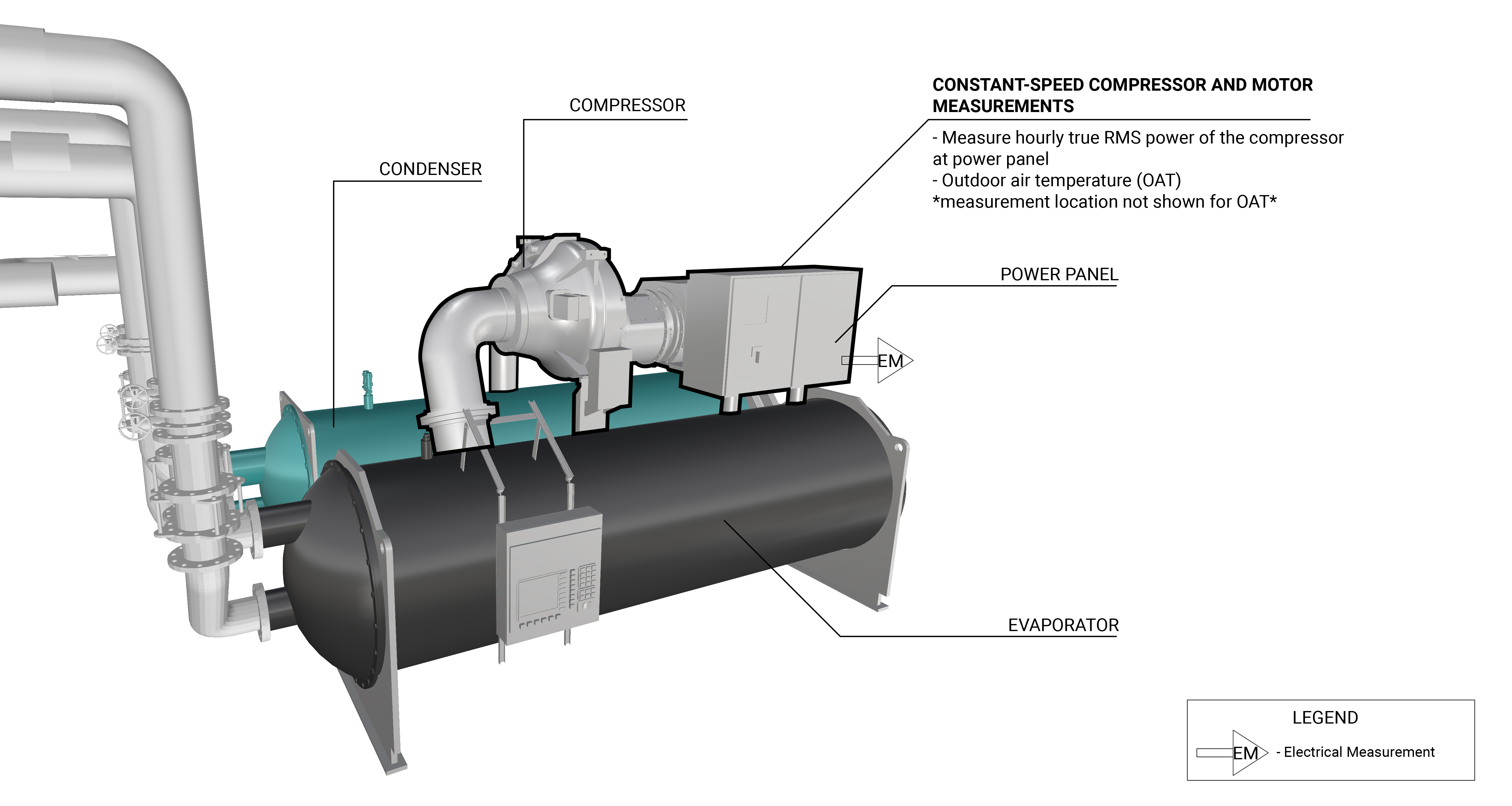
What and How to Measure
Measurements needed to quantify the annual energy consumption and operating characteristics of a compressor and motor:
Measurement Equipment
If you are NYC agency personnel and you’re already familiar with the measurements above, the Field Equipment Lending Library has put together a kit wit all the equipment needed for measuring this component:
Compressor and Motor kit
Use this kit to assess the energy consumption (electricity usage) of a compressor motor connected to a chiller system.
Energy Consumption Quantification
The primary energy source for a compressor is the electricity used to run the compressor motor. The general methodology for quantifying the electricity consumption of a compressor and motor involves measuring their electrical energy use. Depending on operational variability, daily or weekly models incorporating cooling load or a proxy (such as outdoor air temperature) may be developed to better characterize consumption. The typical energy use of a compressor is estimated using its simulated yearly schedule. A more detailed explanation of the calculation methodology is provided below.
How to Quantify
The following downloadable file(s) can be used to calculate energy consumption based on the measurements taken for a constant speed compressor and motor:
Further Reading
- ASHRAE. (2020). HVAC Systems and Equipment. Atlanta, GA: ASHRAE.


